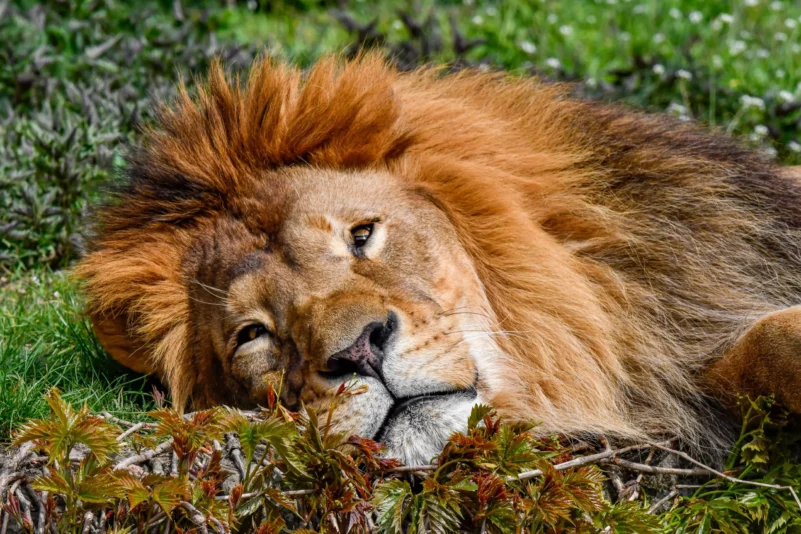
African lion
Panthera leo
African lion
WYGLĄD
Two subspecies of the lion are recognized:
- Panthera leo leo – in central and western Africa and India
- Panthera leo melanochaita – in southern and eastern Africa.
APPEARANCE
Lion is a very muscular and strong cat. The shoulders and front paws are particularly massive and powerful, allowing lions to hunt and overpower large prey. The lion has a even fawn coloration that blends in with the grassy cover of the savanna. Male lions have fringed tails and manes that vary from fairly sparse fur in hot and humid areas to very impressive manes in milder climates. The mane serves to attract females and is an indicator of the condition of the male lion. Young lions have pink noses that gradually become spotted with black spots as they mature. African lions have shorter fur and a less pronounced tail fringe than Asian lions.
DISTRIBUTION AND HABITAT
African lions live in scattered populations throughout sub-Saharan Africa. The lion prefers grassy plains and savannas, scrubby riversides and open forests with shrubs.
BEHAVIOUR
Lions are mainly active at night and dusk. They spend much of the day and night resting and are usually active for four to six hours a day. The lion is the most sociable of all cat species – it lives in complex social systems called herds and exhibits group territorial behaviour. Females cooperate with each other, a behaviour that is unique among cats. Herd leadership is usually exercised by a single male.
FOOD
The lion is a predator that will settle for just about anything, but has a clear preference for medium to large ungulates (100-300 kg) such as wildebeest, zebra, buffalo, giraffe, kudu and kobs. They also catch smaller antelopes such as gazelles and impalas quite frequently. In the case of very large prey such as rhinos, hippos or elephants they only hunt lost or weakened young or very weakened adults.
MAIN THREATS
The main threats to lions are retaliatory killing (using spears, firearms and poisons), a shrinking food base, poaching focused on meat extraction, and excessive or poorly managed trophy hunting.