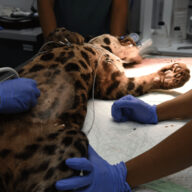
Margay
Leopardus wiedii
Margay
Margay is very diverse genetically, with three phylogeographic groups suggested:
- Leopardus wiedii wiedii in South America south of the Amazon,
- Leopardus wiedii vigens in South America north of the Amazon,
- Leopardus wiedii glauculus in Central America.
APPEARANCE
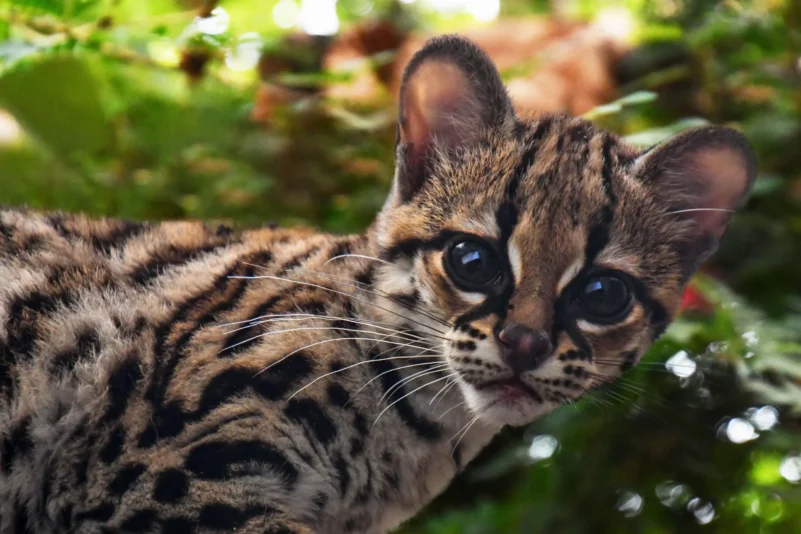
Distinctive features of the margay include the very large and even bulging eyes, giving the muzzle a narrow but prominent appearance. Other features include proportionally very large paws and a very long tail measuring up to 70% of the body length. The margay has dense and soft fur. The basic colour is usually yellowish, but can also change to brownish. The fur is patterned with dark brown or black rosettes. They are usually rounder and less numerous than in other species. The underside of the body is white, the cheeks are marked with two stripes and the back of the ears are black with central white spots, similar to those of ocelot cats. Large dark rings are usually visible on the tail of the margay.
DISTRIBUTION AND HABITAT
The margay is found from the tropical lowlands of Mexico through Central America to Brazil and Paraguay. The southern edge of his range reaches Uruguay and northern Argentina.
Margay is strongly associated with forest habitats and lives mainly in tropical and subtropical evergreen, deciduous/semi-deciduous, foothill moist and very moist forests, and mountain mist forests.
BEHAVIOUR
The margay is a solitary animal. It is a territorial and nocturnal predator, but with some activity during the day as well.
INTERESTING FACT
Margays rest mainly in trees and are thought to be more arboreal and better adapted to living in trees than other cat species. They are excellent climbers and can descend from a trunk head down or hang from a branch on one paw.
FOOD
Most of the prey of margays are nocturnal animals. They feed on small mammals (<0.6 kg), birds and reptiles. Larger medium-sized mammals such as squirrels, rabbits, aguti and small monkeys also fall prey to margays, but in lesser percentages.
MAIN THREATS
Habitat fragmentation and destruction, mainly in the form of deforestation and conversion of native forests into agricultural areas, grazing land and infrastructure (e.g. hydroelectric dams) are considered the main threats today. Illegal hunting still takes place in some areas.